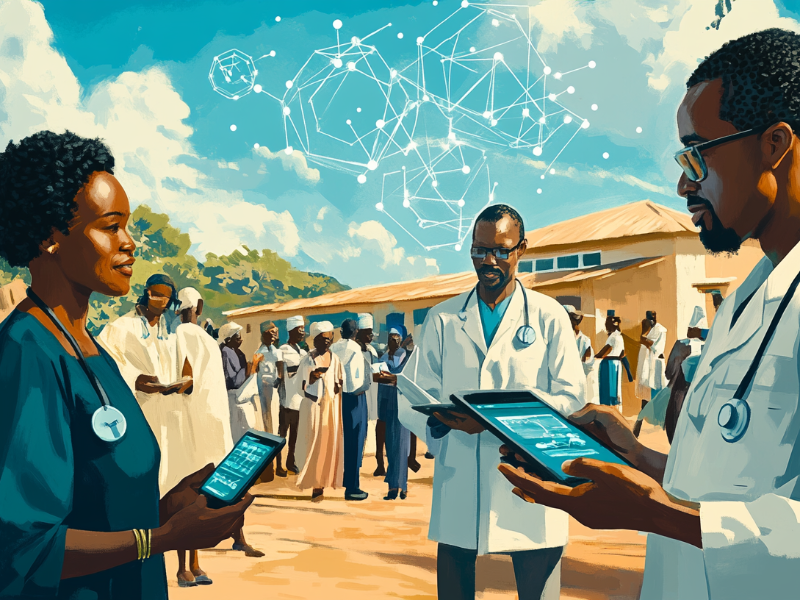
Advancing Health Equity - What Works in Building Trust for Clinical Trials in Africa
Africa, a continent rich in cultural diversity and natural resources, continues to face significant health challenges, including infectious diseases and underrepresentation in clinical research. Addressing these challenges requires not only advancements in healthcare but also the establishment of trust in clinical trials. This article examines the key strategies and partnerships that are successfully fostering trust in clinical research in Africa, ultimately advancing health equity and promoting economic development.
The Importance of Health Equity in Africa
Health equity refers to the idea that everyone, regardless of socioeconomic status, location, or background, should have a fair opportunity to attain their full health potential. In Africa, the healthcare system has long been plagued by inequities due to limited access to healthcare services, shortages in medical personnel, and economic constraints. Clinical trials are essential in identifying treatments and preventive measures for the diseases that disproportionately affect African populations, such as malaria, tuberculosis (TB), and HIV-related cancers. However, the success of these trials hinges on the trust of the communities they seek to serve.
For clinical trials to effectively address health disparities, they must engage underrepresented populations and reflect the diverse genetic makeup of African people. IndyGeneUS AI, a company dedicated to advancing precision medicine for underrepresented populations, is one example of how genomic research can help bridge this gap. By addressing the mistrust that many African populations have historically held toward medical research, organizations like IndyGeneUS are paving the way for more inclusive and effective healthcare solutions.
Challenges to Building Trust in Clinical Trials
Historically, medical research in Africa has been marked by unethical practices, such as exploitative clinical trials and inadequate informed consent processes. These practices have contributed to a deep-rooted mistrust of medical research among many African communities. For example, the infamous Tuskegee Syphilis Study in the United States and other unethical studies conducted in Africa have left a legacy of skepticism that hinders participation in modern clinical trials.
Another challenge is the underrepresentation of African populations in global clinical trials. The lack of African genomic data in medical research has led to treatments and therapeutics that are not tailored to the specific needs of African populations. This absence of representation further perpetuates health inequities and reduces the effectiveness of healthcare interventions on the continent.
To overcome these challenges, clinical trial organizers must develop culturally sensitive and community-oriented approaches that prioritize trust, transparency, and partnership.
Best Practices for Establishing Trust in Clinical Trials
Transparency in Research Processes
One of the most effective ways to build trust in clinical trials is through transparency. Participants must be fully informed about the purpose of the research, the risks involved, and how their data will be used. Clear, open communication is essential to dispel fears and misconceptions surrounding medical research.
Technologies such as blockchain can play a significant role in ensuring transparency. IndyGeneUS AI is leveraging blockchain technology to build the world's largest repository of blockchain-encrypted clinical and genomic data from indigenous and diasporic African populations. IndyGeneUS AI is developing a HIPAA-compliant, patient-centered, decentralized ledger-secured, Precision Health Discovery (PHD) platform that leverages AI/ML algorithms to generate insights using genomic data contributed by research participants from indigenous and African diaspora.[1] This approach allows participants to have confidence in the security and confidentiality of their personal data, which is often a major concern for those considering participation in clinical research.
Engaging Local Communities
Building trust in clinical trials also requires engaging local communities in the research process. This includes involving local healthcare providers, community leaders, and patients in the design and implementation of clinical trials. By collaborating with trusted figures in the community, researchers can overcome the barriers of mistrust and increase participation in clinical trials.
In many African communities, healthcare decisions are made collectively, with input from family members and community leaders. A community-centered approach that respects these cultural norms is key to gaining the trust and participation of local populations. Moreover, researchers must ensure that trial results and benefits are shared with the community, fostering a sense of partnership rather than exploitation.
Culturally Sensitive Communication
Understanding and respecting cultural differences is another critical factor in establishing trust in clinical trials. In many African cultures, Western medical practices are viewed with suspicion, and there is a strong preference for traditional medicine. Researchers must communicate the value and purpose of clinical trials in a way that resonates with local cultural beliefs.
Using local languages and employing culturally appropriate metaphors and analogies can help demystify complex medical concepts. Additionally, employing local healthcare workers and research assistants who understand the cultural nuances of the community can help bridge the gap between researchers and participants.
Building Collaborative Partnerships
Global Partnerships in Clinical Research
Global partnerships play a vital role in building trust for clinical trials in Africa. Collaborations between African healthcare institutions, governments, and international organizations ensure that clinical trials are conducted ethically and transparently, with the input of local stakeholders.
IndyGeneUS AI, for example, has formed partnerships with organizations such as the Aurum Institute and Global Health Innovations to engage millions of patients across Africa in genomic research. These collaborations are not only advancing scientific knowledge but also building trust by involving African institutions and communities in the research process.
The Role of Local Governments and Healthcare Institutions
Local governments and healthcare institutions play a crucial role in ensuring that clinical trials align with the needs and priorities of African communities. Governments can establish regulatory frameworks that protect participants' rights and ensure that clinical trials are conducted ethically. Local healthcare institutions, in turn, can serve as trusted intermediaries between researchers and participants.
In countries such as Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa, governments have established ethics review boards and regulatory agencies to oversee clinical trials and ensure compliance with international standards. These initiatives help build trust by demonstrating a commitment to ethical research practices.
Economic Benefits of Advancing Clinical Trials in Africa
Beyond the immediate health benefits, advancing clinical trials in Africa can contribute to economic development. By participating in clinical trials, African countries can gain access to new treatments and technologies that can reduce healthcare costs and improve public health outcomes. In addition, the clinical research industry can create jobs and stimulate economic growth by attracting investment in healthcare infrastructure and research capacity.
As Africa's population continues to grow, the demand for healthcare services and medical innovation will increase. Clinical trials offer an opportunity to address the continent's healthcare challenges while also fostering economic development through investment in research and development.
Promoting Health Equity through Genomic Data
The Importance of Collecting Diverse Genomic Data
Genomic research has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by enabling the development of personalized treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup. However, the lack of diverse genomic data from African populations has limited the effectiveness of precision medicine in addressing health disparities on the continent.
IndyGeneUS AI is addressing this issue by collecting genomic data from indigenous and Afro-Latin populations, ensuring that precision medicine benefits underrepresented groups. This data is critical for developing treatments for diseases such as malaria, TB, and HIV-related cancers, which disproportionately affect African populations. By contributing to a global repository of genomic data, African countries can ensure that their populations are represented in the future of medical innovation.
Secure Data Handling Encourages Broader Participation
Trust in clinical trials can be enhanced by ensuring that participants' data is handled securely and transparently. The use of blockchain technology to encrypt and protect genomic data is one way to address concerns about privacy and data security.
By employing blockchain-encrypted data repositories, as demonstrated by IndyGeneUS AI, participants can be confident that their personal information is protected. This approach helps build trust and encourages broader participation in clinical research, which is essential for advancing health equity.
Attend the IAEOZ Virtual Summit
As Africa continues to navigate the challenges of health equity and economic development, clinical trials will play a crucial role in addressing the continent's healthcare needs. By building trust and promoting participation in clinical research, African countries can improve public health outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and contribute to global scientific progress.
To learn more about how clinical trials are advancing health equity and economic development in Africa, register to attend the IAEOZ Virtual Summit, taking place from October 17-18, 2024. The summit will bring together global experts to discuss strategies for promoting health equity, advancing clinical trials, and driving economic growth in Africa.
Register today at https://iaeozsummit.com/ to be part of this important conversation and help shape the future of healthcare in Africa.